What is prostatitis know many representatives of the male sex. The disease is manifested by frequent impulses to urinate, pain, erectile dysfunction and other symptoms, which indicate the pathology of the genitourinary system. For more accurate diagnosis is needed to consulting a urologist, who has to find out the cause of the disease and explain what is this disease, what it means to her name, what are the symptoms and treatment.
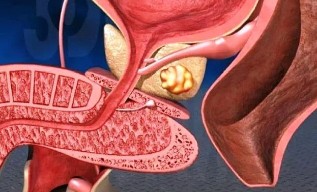
The function of the prostate
Prostate cancer iron — an unpaired organ, which consists of glandular tissue and fibrino-muscle the film, which is located in front of the pelvic area. The upper part adjacent to the bladder, the back — with the rectum, and the front — with the pubic bone.
The basic meaning of prostate cancer – the allocation of a special secret, that provide the sperms viability and motility.
This substance is produced by the acinus – small slices, surrounded by a muscle shell.
To other functions of the prostate include:
- protection against involuntary urination;
- prevention of casting ejaculate into the bladder;
- prevention of infections of the upper flag of the infection of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters).
Job of the prostate control the androgens, estrogens, steroids and pituitary hormones.
Description of the disease
The male prostate gland (prostatitis – wrong spelling) – this is a common pathology of the prostate, accompanied by a reactionary inflammation, impaired urination and sexual disorders. Edema leads to narrowing of the canals of the prostate, preventing the normal outflow of the prostate juice and provokes stagnation.
Most often disease of the prostate in men diagnosed aged 25 – 50 years. Sometimes pathology makes itself known sooner or later.
The causes of
Prostatitis in men develops due to the following reasons:
- Non-transferable. Most often to a deterioration in the functioning of prostate leads to violation of blood circulation and lymph flow in the prostate gland, as well as sluggish phenomena, associated with the occasional ejaculation. Sometimes the pathology develops because of too frequent sexual contacts, or regularly shaking (e.g. for motorcycles).
- Infectious. Inflammation of the prostate gland develops on the background of the penetration of infection. They may be bacteria, viruses or fungi, which fall in the prostate via the blood or lymph from the urethra or remote infected sources (neck, teeth, sinuses, paranasal sinuses).
The factors, which causes prostatitis in men include:
- hypothermia;
- injury;
- genetic predisposition;
- inactive lifestyle or regular physical overwork;
- regular stress;
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- insomnia, lasting enough sleep;
- weak immunity;
- chronic infectious processes;
- tooth decay.
The main cause of the disease is considered a violation of the outflow of the capillary blood, which leads to stagnation, reduced local immunity and reproduction of the bacterial flora.
The impact of adverse factors aggravates the inflammation of the prostate, extending the duration of treatment and contributes to the development of complications.
Types and symptoms
The inflammatory process of the prostate is manifested by:
- pain in the pelvic area (when the outflow of urine, ejaculation, bowel movements);
- the rapid desire to urinate;
- the clotting of blood, mucus, pus from the urethra;
- clouding of the urine;
- decline in libido and other inconveniences.
The degree of severity of clinical symptoms depends on the causes and forms of the disease.
Acute

Acute inflammation of the prostate is usually accompanied by increased body temperature (in the armpit, rectal) and the symptoms of intoxication (pain and joint pain, chills, nausea).
Patient prostate iron compresses the surrounding tissue, nerve endings and raises:
- constipation;
- violation of urination, up to complete cessation of the outflow of urine;
- pain in the lower back, scrotum, groin area.
Acute prostatitis in men more often appears on the background of infection of the prostate pathogenic organisms.
Important! Sometimes an acute inflammation of the prostate will appear on the background, which took place on the eve of the biopsy.
Chronic
Inflammation of the prostate often reveals randomly during a scheduled inspection or examination for another disease.
The progression of the pathology leads to disturbances in the morphology and functioning of the prostate, which is manifested by:
- pain sensations;
- dysuria;
- sexual disorders.
Calculous
This is one of the most common complications of the chronic form of the disease characterized by the formation of stones in the acinus.
How it manifests itself, the affected prostate gland in men, which was calculous inflammation depends on the degree of severity. Of the main clinical symptoms secrete a dull aching pain in the groin, the pubic and testicles.
Prolonged lack of treatment is fraught with the development of inflammation of the seed of man, abscess of the prostate gland, sclerosis of the prostate.
Stagnant
What kind of disease is prostatitis and why it develops, they know, not all representatives of the male gender.
This type of exposed persons:
- a few are moving;
- they have bad habits;
- they are accustomed to a large part of the day they spend sitting down;
- do not lead a regular sexual life;
- practicing each of the sexual acts.
Symptoms when inflammation of the prostate gland on the background of stagnation are identical with the manifestations of chronic and the calculous forms of the disease, and therefore to the refinement of the diagnosis is necessary laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. The first character, which is manifested by stagnant prostatitis in men – the deterioration of erection.
Contagious
The cause of the disease is understandable from the name. Most often, the prostate gland affects the bacteria, are extremely rare, viruses and fungi. In most cases of an infectious inflammatory process of the prostate is a complication of other forms.
To it leads a reduction in the overall or local immunity in the background:
- hypothermia;
- other acute or chronic infection;
- cancer tumors;
- autoimmune disease;
- interruption of the work of neighbouring authorities;
- incorrect lifestyle.
How it manifests itself prostate gland in men, which was inflammation of the infectious type, depends on the current disease. Often complaints resemble the manifestations of acute or chronic prostatitis.
A festering sore
In the advanced cases is in the pathological process involved the entire organ.
The early (catarrhal) form of purulent inflammation takes place with the erased symptoms and vaguely reminiscent of the manifestations of the disease of the urinary bladder – cystitis. With the progression of the pain gets worse and it will appear, expressed symptoms of intoxication.
An abscessed form of the disease the most difficult and often leads to peritonitis, sepsis and death.
Diagnosis
When the primary circulation gland inspected through the anal opening. During palpation the doctor determines the size, structure and contours of the body.
At this stage is put the preliminary diagnosis, which is necessary to confirm through the survey that includes the following laboratory methods:
- extensive and biochemical analysis of blood;
- determination of PSA (prostate specific antigen);
- clinical and bacteriological examination of the urine, prostate secretions, smears from the urethra;
- sensitivity to antibiotics;
- sperm;
- identification of S-reactive protein;
- cystoscopy and histology of the puncture content.
From the instrumental pays:
- rectal ULTRASOUND;
- CT or MRI of the gland and of other organs of the pelvis;
- biopsy.
Diagnosis of diseases of the spend in public or private laboratories.
Principles of treatment

Where and how to treat inflammation of the prostate, a doctor decides on the basis of the results of the analyses. If the patient's condition is satisfactory, then you can make a visit to the clinic and the domestic income of drugs. In the opposite case, the doctor explains the men, the risks associated with the disease, and takes on a stationary treatment. In severe cases the patient hospitalitynet is especially.
Comprehensive
Conservative therapy includes administration of drugs that prevent the cause of the disease, stagnant phenomena and inflammatory process in the prostate gland.
On this list include:
- antibiotics (depending on the results of the antibiogram);
- anti-inflammatories is not the steroid of origin or corticosteroids;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamins and minerals;
- vasodilator drugs (in the absence of contraindications).
In severe pain prescribe analgesics or antispasmodics.
After the removal of the acute phase of the resort to physiotherapy techniques:
- prostate massage;
- electrophoresis;
- microwave therapy;
- ultrasound.
In severe cases, carry out a partial or full prostatectomy (removal of prostate). Prostatitis with stones to treat the identical scheme, but the massage androgen-dependent organ categorically contraindicated.
In domestic conditions
What is prostatitis and how to treat it, they want to know many men. To outpatient treatment is not terminated emergency hospitalization in a hospital, you have to follow all the doctor's recommendations: drink prescribed pills, to avoid provoking factors, and not to self-medicate. In addition to the basic treatment scheme is a useful medicinal herb, which selects the physician.
To eliminate the disease helpful:
- chamomile;
- peony;
- the seeds and leaves of the plantain;
- nettle;
- burdock root;
- the pumpkin seeds.

Prevention
The best prevention of prostatitis in men – regular appeal to the doctors and the adjustment of lifestyle, which must include:
- daily physical load;
- regular sex;
- proper nutrition;
- restful night's sleep.
Stress, bad habits and other precipitating factors, on the contrary, should be removed. Prostatitis in men often leads to erectile dysfunction.
To remove the disease, prescribe drugs from the group inhibitors PDE-5. If that doesn't work, then it is necessary to consult a psychologist.




































